XML
Basic
- XML:eXtensible Markup Language
- XML is a syntax (serialization format) for data sharing and exchange on the Web
- Can translate any data to XML
- Can ship XML over the Web (HTTP)
- Can input XML into any application
XML Structure
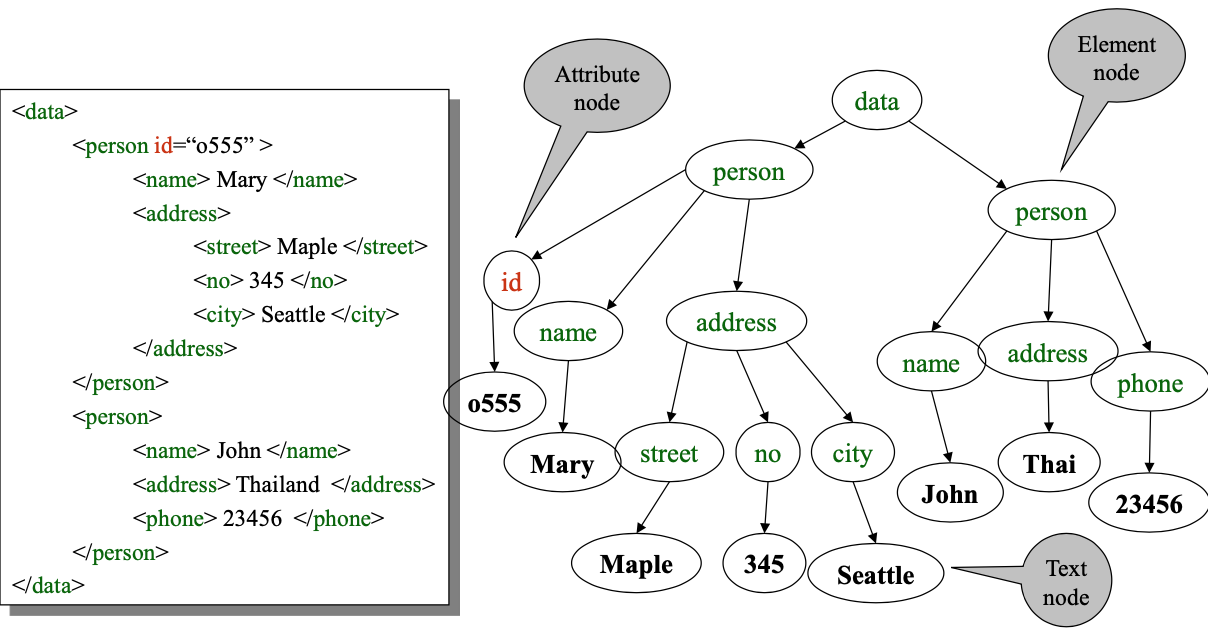
- XML is self-describing
- Schema elements become part of the data(关系型数据记录中schema不算是内容,但是在xml中节点自身也携带内容信息)
- XML is semi-structured
- missing attributes (could be represented as null in table)
- repeated attributes (impossible in table)
- Attributes with different types in different objects
- Nested structures
- Heterogeneous contents
- an XML document has a single root element
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
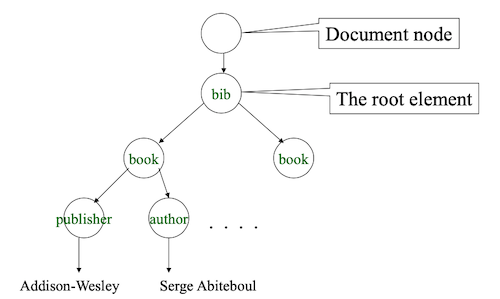
| example:
<bib>
...
<book price="35">
<publisher>Addison-Wesley</publisher>
<author>Serge Abiteboul</author>
<author>
<first-name>Rick</first-name>
<last-name>Hull</last-name>
</author>
<author age="20">Victor Vianu</author>
<title>Foundations of Databases</title>
<year>1995</year>
<price>38.8</price>
</book>
<book price="55">
<publisher>Freeman</publisher>
<author>Jeffrey D. Ullman</author>
<title>Principles of Database and Knowledge Base Systems</title>
<year>1998</year>
</book>
...
</bib>
|
Querying XML Data
XPath: simple navigation through the tree
lxml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| $ pip install lxml
from lxml import etree
f = open('bibs.xml')
tree = etree.parse(f)
print(etree.tostring(tree, pretty_print=True))
for element in tree.xpath("//author"):
print(etree.tostring(element))
print(element.tag, element.text)
|

