Blocking and Relational Entity Resolution
前情提要
Entity Resolution 主要分成如下四个
- Coreference 文本与文本之间找同一个entity
- Entity linking 文本与KG中找对应entity -> Integrating New Candidates
- Deduplication 一个KG之间的聚类 -> Merging Ambiguous Entities
- Record linkage 两个不同KG之间entity的对应 -> Combining KGs
Blocking
为什么需要Blocking -> reduce the number of comparisons
- Comparing each entity with all other entities is too computationally demanding –> O(N^2)
- If partition entities into N ”blocks”– O(N)
- Make only within block comparisons, so if largest block is log N in size –> O(NlogN^2)
Blocking 分类
Disjoint Blocking: Each mention appears in one block.(=Set Partition)
Non-disjoint Blocking: Mentions can appear in more than one block.
Blocking一般的情形
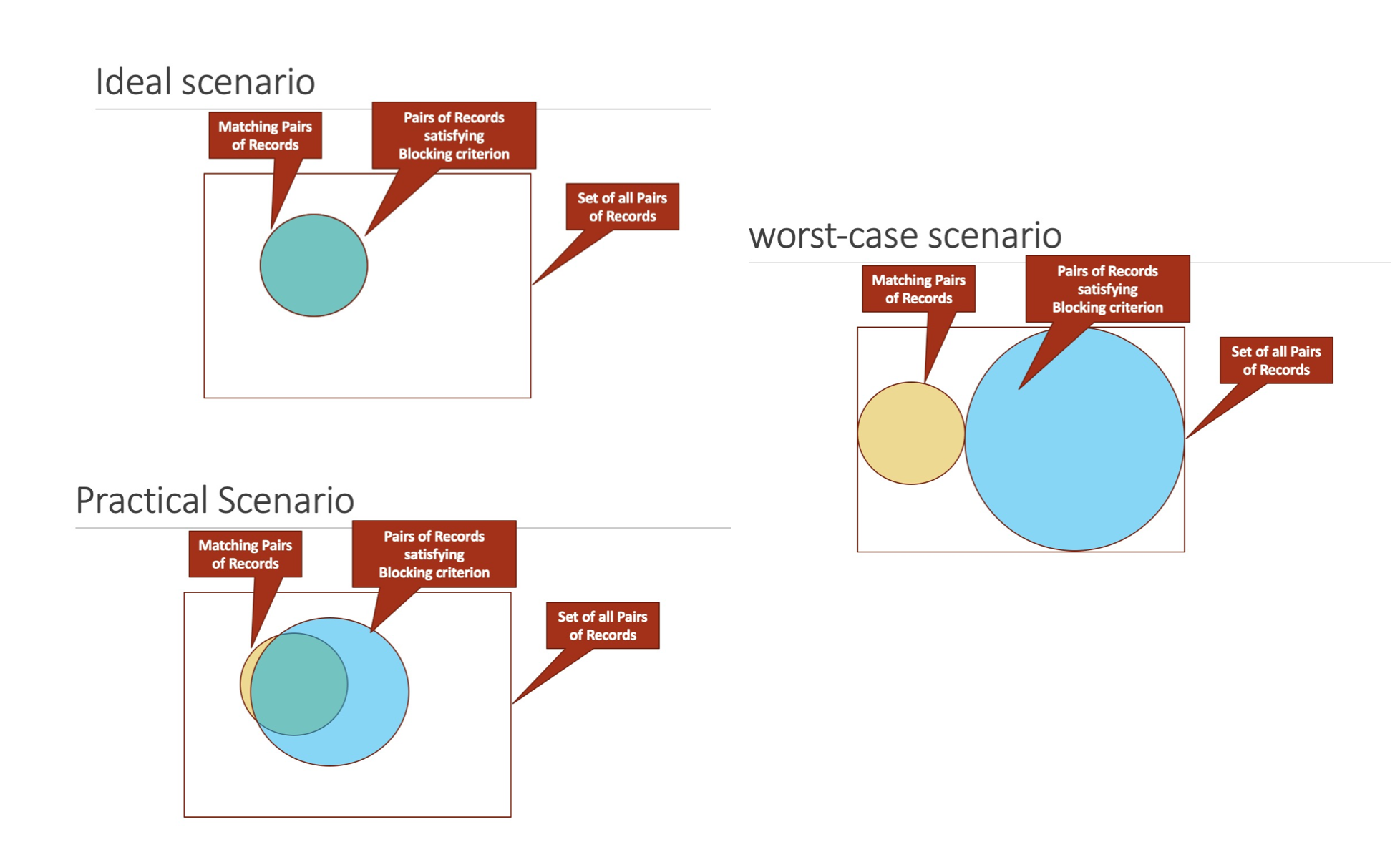
Blocking衡量指标
- Efficiency: Blue/Grey
- Recall: Green/Yellow
- Precision: Green/Blue
- Max Canopy Size: 包含mentions个数最多的block的mentions个数
Blocking方式
Feature-based blocking keys
思想: 通过选择实体的某一个或者多个属性作为key,将包含该key的实体放在同一个block下,对每个block再进行entity resolution
例子:
First three characters of last name
City + State + Zip
Character or Token n-grams
Minimum infrequent n-grams
Clustering or sorting
Sorted Neighborhood Blocking
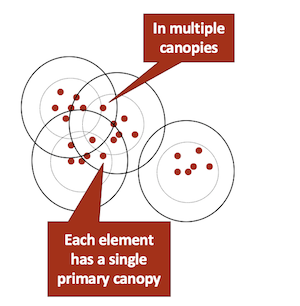
思想: 通过选择实体的某一个属性,根据该属性对实体进行排序,使用一个窗格,窗格内的实体划分到一个block中去Canopy Clustering
Input: Mentions M, x is an entity
d(x,y), a distance metric
thresholds T1 > T2
思想:
- Pick a random element x from M
- Create new canopy Cx using mentions y s.t. d(x,y) < T1
- Delete all mentions y from M s.t. d(x,y) < T2
- Return to Step 1 if M is not empty
Hashing
思想:
- Each block Ci is associated with a hash key hi.
- Mention x is hashed to Ci if hash(x) = hi.
- Within a block, all pairs are compared.
- Each hash function results in disjoint blocks.
Blocking选择考虑因素
- key的选择:learn the keys, or use expert knowledge/heuristics?
- Schema awareness: what do we know about the attributes?
- Key type: exact equality, similarity-based, or hybrid 相同的key放到一个block还是相似放一个block
- Redundancy: entity in one or multiple blocks? Does matching in multiple blocks increase the match probability
- Frequency limits
- Adaptive keys based on frequency
- Learning keys based on data
Learning to block
Using one or more blocking predicates may be insufficient => Construct blocking predicates by combining simple predicates
Collective Relational Entity Resolution
策略: Using PSL for collective KG ER
- Encode ER dependencies in a set of rules
- Use soft-logic values to capture similarities
- Use logic to capture the constraints
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!